介绍
- PLEG 全称叫 Pod Lifecycle Event Generator,即 Pod 生命周期事件生成器
- pleg通过定时的执行relist方法调用容器运行时获取pod信息
- 遍历pod中的容器对比缓存中的状态,生成状态变化事件交给syncloop事件循环处理
整体工作流程
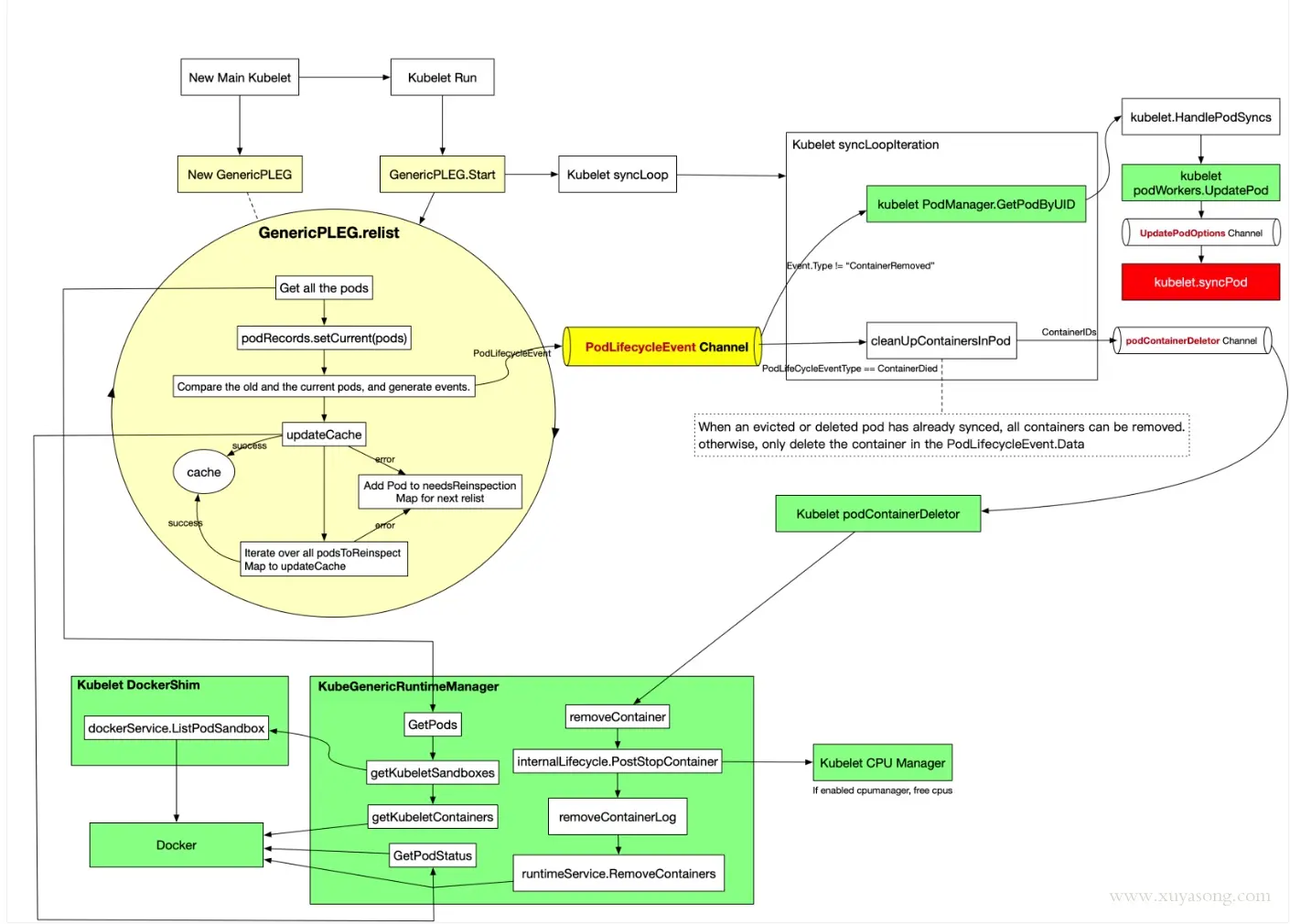
函数调用
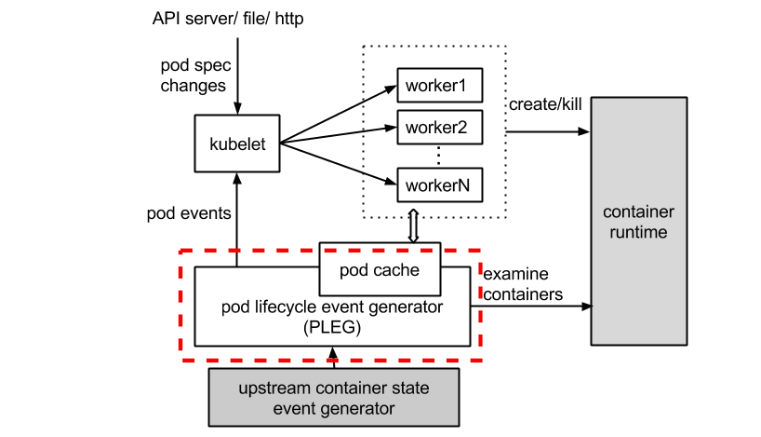
什么是 PLEG
- PLEG 全称叫 Pod Lifecycle Event Generator,即 Pod 生命周期事件生成器
- 实际上它只是 Kubelet 中的一个模块
- 主要职责就是通过每个匹配的 Pod 级别事件来调整容器运行时的状态,并将调整的结果写入缓存,使 Pod 的缓存保持最新状态
为什么需要PLEG
在 Kubernetes 中,每个节点上都运行着一个守护进程 Kubelet 来管理节点上的容器,调整容器的实际状态以匹配 spec 中定义的状态,具体来说,Kubelet 需要对两个地方的更改做出及时的回应
- Pod spec 中定义的状态
- 容器运行时的状态
对于POD: Kubelet 会从多个数据来源 watch Pod spec 中的变化
对于容器: Kubelet 会定期(例如,10s)轮询容器运行时,以获取所有容器的最新状态。
引发问题:
- 随着 Pod 和容器数量的增加,会产生不可忽略的开销,并且会由于 Kubelet 的并行操作而加剧这种开销(为每个 Pod 分配一个 goruntine,用来获取容器的状态)
- 轮询带来的周期性大量并发请求会导致较高的 CPU 使用率峰值(即使 Pod 的定义和容器的状态没有发生改变),降低性能。最后容器运行时可能不堪重负,从而降低系统的可靠性,限制 Kubelet 的可扩展性。
PLEG出现
为了降低 Pod 的管理开销,提升 Kubelet 的性能和可扩展性,引入了 PLEG,改进了之前的工作方式:
- 减少空闲期间的不必要工作(例如 Pod 的定义和容器的状态没有发生更改)。
- 减少获取容器状态的并发请求数量。
理论知识讲完了,taik is cheap show me your code
PLEG接口解读
D:\go_path\src\github.com\kubernetes\kubernetes\pkg\kubelet\pleg\pleg.go
//PodLifecycleEventGenerator 包含用于生成Pod生命周期事件的函数
type PodLifecycleEventGenerator interface {
Start()
Watch() chan *PodLifecycleEvent
Healthy() (bool, error)
}
PLEG接口实际实现
PodLifecycleEventGenerator接口实现: GenericPLEG
type GenericPLEG struct {
// The period for relisting.
relistPeriod time.Duration
// The container runtime.
runtime kubecontainer.Runtime
// The channel from which the subscriber listens events.
eventChannel chan *PodLifecycleEvent
// The internal cache for pod/container information.
podRecords podRecords
// Time of the last relisting.
relistTime atomic.Value
// Cache for storing the runtime states required for syncing pods.
cache kubecontainer.Cache
// For testability.
clock clock.Clock
// Pods that failed to have their status retrieved during a relist. These pods will be
// retried during the next relisting.
podsToReinspect map[types.UID]*kubecontainer.Pod
}
pkg/kubelet/pleg/generic.go
GenericPLEG 初始化
// NewGenericPLEG instantiates a new GenericPLEG object and return it.
func NewGenericPLEG(runtime kubecontainer.Runtime, channelCapacity int,
relistPeriod time.Duration, cache kubecontainer.Cache, clock clock.Clock) PodLifecycleEventGenerator {
return &GenericPLEG{
relistPeriod: relistPeriod,
runtime: runtime,
eventChannel: make(chan *PodLifecycleEvent, channelCapacity),
podRecords: make(podRecords),
cache: cache,
clock: clock,
}
}
在kubelet启动时会被调用到
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
klet.pleg = pleg.NewGenericPLEG(klet.containerRuntime, plegChannelCapacity, plegRelistPeriod, klet.podCache, clock.RealClock{})
klet.runtimeState = newRuntimeState(maxWaitForContainerRuntime)
// 责任链模式 会不断调用Healthy() (bool, error)
klet.runtimeState.addHealthCheck("PLEG", klet.pleg.Healthy)
if _, err := klet.updatePodCIDR(kubeCfg.PodCIDR); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Pod CIDR update failed")
}
而后追踪可以发现在kubelet的syncLoop中会定时调用runtimeState.runtimeErrors做健康检测
for {
if err := kl.runtimeState.runtimeErrors(); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Skipping pod synchronization")
// exponential backoff
time.Sleep(duration)
duration = time.Duration(math.Min(float64(max), factor*float64(duration)))
continue
}
// reset backoff if we have a success
duration = base
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now())
if !kl.syncLoopIteration(updates, handler, syncTicker.C, housekeepingTicker.C, plegCh) {
break
}
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now())
}
在runtimeState的runtimeErrors中可以看到就是遍历healthChecks的hc,然后执行hc的fn方法
for _, hc := range s.healthChecks {
if ok, err := hc.fn(); !ok {
errs = append(errs, fmt.Errorf("%s is not healthy: %v", hc.name, err))
}
}
对应的pleg 的healthy方法如下
- 获取上一次的relist时间
- 和当前时间做差值,判断是否大于relistThreshold = 3 * time.Minute (why?每一次relist后会更新relistTime)
- 如果大于3分钟证明relist耗时太久或者挂了,那么健康检查失败
// Healthy check if PLEG work properly.
// relistThreshold is the maximum interval between two relist.
func (g *GenericPLEG) Healthy() (bool, error) {
relistTime := g.getRelistTime()
if relistTime.IsZero() {
return false, fmt.Errorf("pleg has yet to be successful")
}
// Expose as metric so you can alert on `time()-pleg_last_seen_seconds > nn`
metrics.PLEGLastSeen.Set(float64(relistTime.Unix()))
elapsed := g.clock.Since(relistTime)
if elapsed > relistThreshold {
return false, fmt.Errorf("pleg was last seen active %v ago; threshold is %v", elapsed, relistThreshold)
}
return true, nil
}
pleg的启动
在kubelet的启动时调用了pleg的start
// Start the pod lifecycle event generator.
kl.pleg.Start()
- 对应的pleg start方法也很清晰,就是定时执行relist
// Start spawns a goroutine to relist periodically.
func (g *GenericPLEG) Start() {
go wait.Until(g.relist, g.relistPeriod, wait.NeverStop)
}
relist解析
- 首先就是耗时的metrics记录
if lastRelistTime := g.getRelistTime(); !lastRelistTime.IsZero() {
metrics.PLEGRelistInterval.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(lastRelistTime))
}
timestamp := g.clock.Now()
defer func() {
metrics.PLEGRelistDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(timestamp))
}()
// Get all the pods.
podList, err := g.runtime.GetPods(true)
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "GenericPLEG: Unable to retrieve pods")
return
}
g.updateRelistTime(timestamp)
// update running pod and container count
updateRunningPodAndContainerMetrics(pods)
- 从代码中可以看到对应的统计细节
- 首先构建以容器运行状态为key,value是个数的 map
- 然后变量pods,再遍历容器
- 将containerStateCount按状态计数
- 然后根据每一个pod只有一个运行的sandbox 计算运行的pod数量
- 最后打点即可
- updateRunningPodAndContainerMetrics 代码如下
func updateRunningPodAndContainerMetrics(pods []*kubecontainer.Pod) {
runningSandboxNum := 0
// intermediate map to store the count of each "container_state"
containerStateCount := make(map[string]int)
for _, pod := range pods {
containers := pod.Containers
for _, container := range containers {
// update the corresponding "container_state" in map to set value for the gaugeVec metrics
containerStateCount[string(container.State)]++
}
sandboxes := pod.Sandboxes
for _, sandbox := range sandboxes {
if sandbox.State == kubecontainer.ContainerStateRunning {
runningSandboxNum++
// every pod should only have one running sandbox
break
}
}
}
for key, value := range containerStateCount {
metrics.RunningContainerCount.WithLabelValues(key).Set(float64(value))
}
// Set the number of running pods in the parameter
metrics.RunningPodCount.Set(float64(runningSandboxNum))
}
- 遍历更新pod record的current
g.podRecords.setCurrent(pods)
- 遍历对比旧的pod和当前pod,生成事件
for pid := range g.podRecords {
oldPod := g.podRecords.getOld(pid)
pod := g.podRecords.getCurrent(pid)
// Get all containers in the old and the new pod.
allContainers := getContainersFromPods(oldPod, pod)
- getContainersFromPods就是遍历pod获取所有的容器
func getContainersFromPods(pods ...*kubecontainer.Pod) []*kubecontainer.Container {
cidSet := sets.NewString()
var containers []*kubecontainer.Container
for _, p := range pods {
if p == nil {
continue
}
for _, c := range p.Containers {
cid := string(c.ID.ID)
if cidSet.Has(cid) {
continue
}
cidSet.Insert(cid)
containers = append(containers, c)
}
// Update sandboxes as containers
// TODO: keep track of sandboxes explicitly.
for _, c := range p.Sandboxes {
cid := string(c.ID.ID)
if cidSet.Has(cid) {
continue
}
cidSet.Insert(cid)
containers = append(containers, c)
}
}
return containers
}
- 然后遍历所有的容器进行event判定
for _, container := range allContainers {
events := computeEvents(oldPod, pod, &container.ID)
for _, e := range events {
updateEvents(eventsByPodID, e)
}
}
computeEvents解析
- 使用getContainerState 分别获取oldState和newState,进行对比
func computeEvents(oldPod, newPod *kubecontainer.Pod, cid *kubecontainer.ContainerID) []*PodLifecycleEvent {
var pid types.UID
if oldPod != nil {
pid = oldPod.ID
} else if newPod != nil {
pid = newPod.ID
}
oldState := getContainerState(oldPod, cid)
newState := getContainerState(newPod, cid)
return generateEvents(pid, cid.ID, oldState, newState)
}
getContainerState解析
- 将初始状态记为plegContainerNonExistent non-existent
// Default to the non-existent state.
state := plegContainerNonExistent
if pod == nil {
return state
}
c := pod.FindContainerByID(*cid)
if c != nil {
return convertState(c.State)
}
- 然后调用convertState 获取状态
convertState 解析
- 可以看到就是判断容器的state,然后转化为plegContainer state
- ContainerStateCreated 对应的是 plegContainerUnknown ,意思是容器被创建出来但是没有启动
- ContainerStateRunning 对应的是plegContainerRunning ,代表容器正常运行中
- ContainerStateExited 对应的是plegContainerExited ,代表容器运行结束了
- ContainerStateUnknown 对应的是plegContainerUnknown ,代表容器当前处于 restarting, paused, dead
func convertState(state kubecontainer.State) plegContainerState {
switch state {
case kubecontainer.ContainerStateCreated:
// kubelet doesn't use the "created" state yet, hence convert it to "unknown".
return plegContainerUnknown
case kubecontainer.ContainerStateRunning:
return plegContainerRunning
case kubecontainer.ContainerStateExited:
return plegContainerExited
case kubecontainer.ContainerStateUnknown:
return plegContainerUnknown
default:
panic(fmt.Sprintf("unrecognized container state: %v", state))
}
}
computeEvents中调用generateEvents对比新老状态
generateEvents解析
- 如果新老状态相等则返回
if newState == oldState {
return nil
}
-
然后对newState当前状态进行判定,产生对应的事件
- plegContainerRunning 产生 ContainerStarted 事件,代表容器启动了
- plegContainerExited 产生 ContainerDied 事件,代表容器死掉了
- plegContainerUnknown 产生 ContainerDied 事件,代表容器死掉了
- plegContainerExited 产生 ContainerChanged 事件,代表容器状态改变了
-
如果newState是plegContainerNonExistent,则需要对旧状态进行判断
- oldState是 plegContainerExited 产生ContainerRemoved ,代表exited的容器被删除了
- oldState是 其他状态, 产生ContainerDied ,代表容器死掉了
遍历产生的event
- 忽略ContainerChanged类型,其余类型发送给eventChannel
for i := range events {
// Filter out events that are not reliable and no other components use yet.
if events[i].Type == ContainerChanged {
continue
}
select {
case g.eventChannel <- events[i]:
default:
metrics.PLEGDiscardEvents.Inc()
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Event channel is full, discard this relist() cycle event")
}
同时在kubelet的syncloop中会启动 pleg的watch
plegCh := kl.pleg.Watch()
- 同时将获取到的plegCh变更chan 同步给syncLoopIteration处理
if !kl.syncLoopIteration(updates, handler, syncTicker.C, housekeepingTicker.C, plegCh) {
break
}
- 在syncLoopIteration中判断event的类型,忽略其中的ContainerStarted,只是更新一下lastContainerStartedTime
case e := <-plegCh:
if e.Type == pleg.ContainerStarted {
// record the most recent time we observed a container start for this pod.
// this lets us selectively invalidate the runtimeCache when processing a delete for this pod
// to make sure we don't miss handling graceful termination for containers we reported as having started.
kl.lastContainerStartedTime.Add(e.ID, time.Now())
}
- 如果event不是 remove ,需要判断在podManager是否存在pod
if isSyncPodWorthy(e) {
// PLEG event for a pod; sync it.
if pod, ok := kl.podManager.GetPodByUID(e.ID); ok {
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop (PLEG): event for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "event", e)
handler.HandlePodSyncs([]*v1.Pod{pod})
} else {
// If the pod no longer exists, ignore the event.
klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop (PLEG): pod does not exist, ignore irrelevant event", "event", e)
}
}
- 如果存在,调用HandlePodSyncs 回调,调用dispatch分发给worker执行
// HandlePodSyncs is the callback in the syncHandler interface for pods
// that should be dispatched to pod workers for sync.
func (kl *Kubelet) HandlePodSyncs(pods []*v1.Pod) {
start := kl.clock.Now()
for _, pod := range pods {
mirrorPod, _ := kl.podManager.GetMirrorPodByPod(pod)
kl.dispatchWork(pod, kubetypes.SyncPodSync, mirrorPod, start)
}
}
- 如果不存在,只是打印一条日志即可
- 如果类型是ContainerDied那就调用 cleanUpContainersInPod清理pod中的容器
if e.Type == pleg.ContainerDied {
if containerID, ok := e.Data.(string); ok {
kl.cleanUpContainersInPod(e.ID, containerID)
}
cleanUpContainersInPod分析
- 获取pod中需要删除的containerid,传入p.worker中
func (p *podContainerDeletor) deleteContainersInPod(filterContainerID string, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus, removeAll bool) {
containersToKeep := p.containersToKeep
if removeAll {
containersToKeep = 0
filterContainerID = ""
}
for _, candidate := range getContainersToDeleteInPod(filterContainerID, podStatus, containersToKeep) {
select {
case p.worker <- candidate.ID:
default:
klog.InfoS("Failed to issue the request to remove container", "containerID", candidate.ID)
}
}
}
- 而worker chan的消费端在newPodContainerDeletor启动的
go wait.Until(func() {
for {
id := <-buffer
if err := runtime.DeleteContainer(id); err != nil {
klog.InfoS("DeleteContainer returned error", "containerID", id, "err", err)
}
}
}, 0, wait.NeverStop)
- 底层调用的就是 runtime.DeleteContainer删除容器
重点总结:
- PLEG 全称叫 Pod Lifecycle Event Generator,即 Pod 生命周期事件生成器
- pleg通过定时的执行relist方法调用容器运行时获取pod信息
- 遍历pod中的容器对比缓存中的状态,生成状态变化事件交给syncloop事件循环处理
