本文将介绍如何优雅使用echart可视化Prometheus内的监控数据,包含大量实际代码,前端使用vue3+echart5,后端使用go编写,阅读前需要有一定的go与vue3开发基础
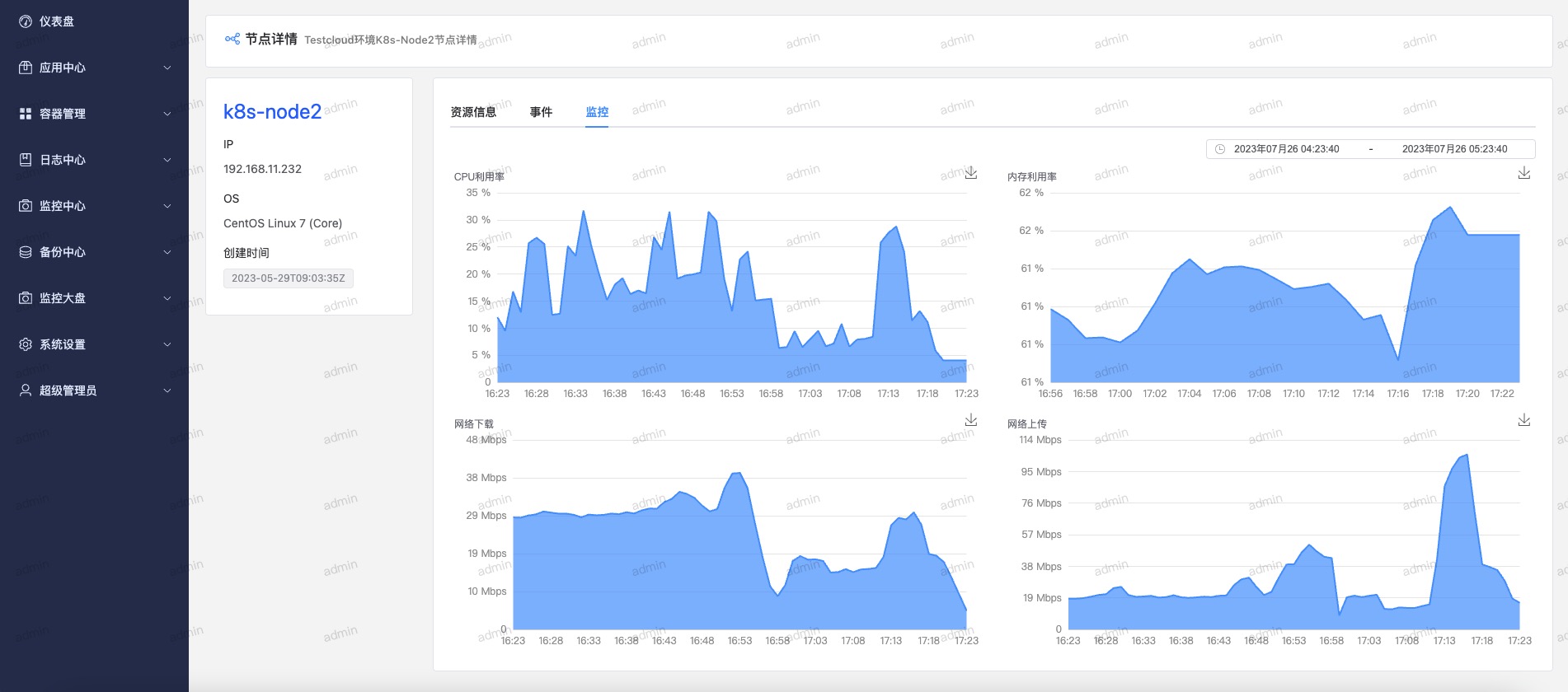
首先先看一下成果
注: 截图来自于我司内部运维平台
从Prometheus中获取指标数据
首先普罗米修斯是用go语言编写的,所以官方是提供了go语言版本的sdk,翻看源码实际上就是向普罗米修斯发起接口调用,我们可以很方便的使用PrometheusSDK来获取数据,代码如下
package apis
import (
"context"
"errors"
"fmt"
"strconv"
"strings"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/prometheus/client_golang/api"
v1 "github.com/prometheus/client_golang/api/prometheus/v1"
"github.com/prometheus/common/model"
"kubegems.io/kubegems/pkg/service/handlers"
"kubegems.io/kubegems/pkg/utils/clusterinfo"
"kubegems.io/kubegems/pkg/utils/prometheus"
)
// 用于动态计算步长
func dynamicTimeStep(start time.Time, end time.Time) time.Duration {
interval := end.Sub(start)
if interval < 30*time.Minute {
return 30 * time.Second // 30 分钟以内,step为30s, 返回60个点以内
} else {
return interval / 60 // 返回60个点,动态step
}
}
// 初始化客户端,以后所有的API请求都会使用
func NewPrometheusHandler(server string) (*prometheusHandler, error) {
client, err := api.NewClient(api.Config{Address: server})
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &prometheusHandler{client: client}, nil
}
// 获取Vector单个数据
func (p *prometheusHandler) Vector(c *gin.Context) {
query := c.Query("query")
v1api := v1.NewAPI(p.client)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 60*time.Second)
defer cancel()
obj, _, err := v1api.Query(ctx, query, time.Now())
if err != nil {
NotOK(c, err)
return
}
if notnull, _ := strconv.ParseBool(c.Query("notnull")); notnull {
if obj.String() == "" {
NotOK(c, errors.New("空查询"))
return
}
}
OK(c, obj)
}
// 获取Matrix一组数据
func (p *prometheusHandler) Matrix(c *gin.Context) {
query := c.Query("query")
start := c.Query("start")
end := c.Query("end")
step, _ := strconv.Atoi(c.Query("step"))
v1api := v1.NewAPI(p.client)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 60*time.Second)
defer cancel()
s, _ := time.Parse("2006-01-02T15:04:05Z", start)
e, _ := time.Parse("2006-01-02T15:04:05Z", end)
r := v1.Range{
Start: s,
End: e,
}
if step > 0 {
r.Step = time.Duration(step) * time.Second
} else {
// 不传step就动态控制
r.Step = dynamicTimeStep(r.Start, r.End)
}
obj, _, err := v1api.QueryRange(ctx, query, r)
if err != nil {
handlers.NotOK(c, err)
return
}
handlers.OK(c, obj)
}
使用上面的两个函数,入参是promql语句,就可以获取到指标数据了,解释一下Matrix于Vector的区别
向量vector是指 单个时间点的指标样本,矩阵matrix是一组 时间点的样本。无论是vector还是matrix,他们都可以是多个指标,不过区别在于指标的样本 是单个时间点的,还是一组时间节点的
封装Echarts
因为最终目的是要在前端展示的,这里用到了百度的开源库echarts,同时呢为了简化使用需要进行一定的封装,不过笔者没有进行大量的封装,基本上就是能用就行
封装echart为vue组件,代码如下
<template>
<div ref="scEcharts" :style="{height:height, width:width}"></div>
</template>
<script>
import * as echarts from 'echarts';
import T from './echarts-theme-T.js';
echarts.registerTheme('T', T);
const unwarp = (obj) => obj && (obj.__v_raw || obj.valueOf() || obj);
export default {
...echarts,
name: "scEcharts",
props: {
height: { type: String, default: "100%" },
width: { type: String, default: "100%" },
nodata: {type: Boolean, default: false },
option: { type: Object, default: () => {} }
},
data() {
return {
isActivat: false,
myChart: null
}
},
watch: {
option: {
deep:true,
handler (v) {
unwarp(this.myChart).setOption(v);
}
}
},
computed: {
myOptions: function() {
return this.option || {};
}
},
activated(){
if(!this.isActivat){
this.$nextTick(() => {
this.myChart.resize()
})
}
},
deactivated(){
this.isActivat = false;
},
mounted(){
this.isActivat = true;
this.$nextTick(() => {
this.draw();
})
},
methods: {
draw(){
var myChart = echarts.init(this.$refs.scEcharts, 'T');
myChart.setOption(this.myOptions);
this.myChart = myChart;
window.addEventListener('resize', () => myChart.resize());
}
}
}
</script>
同时呢为了简化配置,我们将主题单独抽离出来一个文件echarts-theme-T.js,文件内容如下
const T = {
"color": [
"#409EFF",
"#36CE9E",
"#f56e6a",
"#626c91",
"#edb00d",
"#909399"
],
'grid': {
'left': '3%',
'right': '3%',
'bottom': '10',
'top': '40',
'containLabel': true
},
"legend": {
"textStyle": {
"color": "#999"
},
"inactiveColor": "rgba(128,128,128,0.4)"
},
"categoryAxis": {
"axisLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "rgba(128,128,128,0.2)",
"width": 1
}
},
"axisTick": {
"show": false,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#333"
}
},
"axisLabel": {
"color": "#999"
},
"splitLine": {
"show": false,
"lineStyle": {
"color": [
"#eee"
]
}
},
"splitArea": {
"show": false,
"areaStyle": {
"color": [
"rgba(255,255,255,0.01)",
"rgba(0,0,0,0.01)"
]
}
}
},
"valueAxis": {
"axisLine": {
"show": false,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "#999"
}
},
"splitLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"color": "rgba(128,128,128,0.2)"
}
}
}
}
export default T
如何使用这个组件呢?只需要传递关键的option就可以了,使用过echart的同学们都清楚,option实例在官网上有很多,在这里就不再赘述
https://echarts.apache.org/zh/index.html
<echarts :option=option />
处理指标中的各种单位
实际上处理单位是最为复杂的一部分了,因为promtheus返回的数据全都是字节或者其他小单位,如果直接使用会造成x轴数据杂乱,不利于观察,这里我们需要用到format函数进行处理格式化
const formatter = (value: number | string): string => {
// 如果值为0,返回字符串'0'
if (value === 0) return '0';
// 如果值为NaN,返回字符串'0'
if (isNaN(value as number)) return '0';
// 如果值为空或undefined,返回空字符串
if (!value) return '';
// 调用unitBase函数获取单位、缩放因子和新的值
const { scaleNum, unitType, newValue } = unitBase(0, props.type, value);
value = newValue;
// 如果没有单位类型,直接返回缩放数字串
if (!unitType) {
return scaleNum;
}
// 如果单位类型是'duration',调用beautifyDurationUnit函数格式化值并返回
else if (unitType === 'duration') {
return beautifyDurationUnit(value.toString());
}
// 其他情况下调用beautifyUnit函数格式化值并返回
else {
return beautifyUnit(value.toString(), parseFloat(scaleNum), allUnit[unitType], unitType);
}
};
// 获取单位类型的辅助函数
const getType = (): string | undefined => {
// 如果props.unit为'short',返回'short'
if (props.unit === 'short') {
return 'short';
}
// 否则遍历allUnit对象,找到包含props.unit的单位类型
return Object.keys(allUnit).find((u) => {
const inUnit = allUnit[u].some((n) => {
return n.toLocaleLowerCase() === props.unit.toLocaleLowerCase();
});
return inUnit;
});
};
// 计算单位、缩放因子和新的值的辅助函数
const unitBase = (
scaleNum: number,
unitType: string,
value: string | number,
): { scaleNum: string; unitType: string; newValue: number | string } => {
// 根据单位类型设置不同的缩放因子
switch (unitType) {
case 'memory':
case 'storage':
case 'network':
case 'bytes':
case 'bytes/sec':
scaleNum = 1024;
break;
case 'cpu':
case 'timecost':
case 'short':
scaleNum = 1000;
break;
case 'seconds':
scaleNum = 60;
break;
case 'percent':
scaleNum = 100;
break;
case 'reqrate':
break;
case 'duration':
break;
case '%':
// 如果单位类型为%,返回格式化后的字符串,单位类型为空
return {
scaleNum: `${parseFloat(value as string).toFixed(props.precision)} ${unitType}`,
unitType: '',
newValue: value,
};
break;
default:
if (props.unit) {
// 获取单位类型
unitType = getType() as string;
if (unitType) {
// 如果存在单位类型,递归调用unitBase函数继续处理
return unitBase(scaleNum, unitType, value);
} else {
// 如果不存在单位类型,返回格式化后的字符串,单位类型为空
return {
scaleNum: `${parseFloat(value as string).toFixed(props.precision)} ${props.unit}`,
unitType: '',
newValue: value,
};
}
}
// 如果没有单位类型,返回格式化后的字符串,单位类型为空
return {
scaleNum: `${parseFloat(value as string).toFixed(props.precision)} ${unitType}`,
unitType: '',
newValue: value,
};
}
// 如果有单位类型,并且有指定单位
if (props.unit) {
const d = allUnit[unitType].findIndex((u) => {
return u.toLocaleLowerCase() === props.unit.toLocaleLowerCase();
});
// 根据单位类型和指定单位进行换算
if (unitType === 'duration') {
if (d <= 3) {
value = (value as number) * Math.pow(1000, d);
} else if (d <= 5) {
value = (value as number) * Math.pow(1000, 3) * Math.pow(60, d - 3);
} else if (d <= 6) {
value = (value as number) * Math.pow(1000, 3) * Math.pow(60, 2) * Math.pow(24, d - 5);
} else {
value = (value as number) * Math.pow(1000, 3) * Math.pow(60, 2) * Math.pow(24, 1) * Math.pow(7, d - 6);
}
} else if (unitType === 'short') {
value = (value as number) * Math.pow(scaleNum, 3);
} else {
value = (value as number) * Math.pow(scaleNum, d);
}
}
return { scaleNum: scaleNum.toString(), unitType: unitType, newValue: value };
};
// 格式化值和单位的辅助函数
const beautifyUnit = (num: string, sclaeNum: number, units: string[] = [], unitType = ''): string => {
let result = parseFloat(num);
for (const index in units) {
if (Math.abs(result) <= sclaeNum || parseInt(index) === units?.length - 1) {
if (unitType === 'percent') {
// 如果单位类型是百分比,特殊处理
if (result > 1 && result < 1.001) {
return `${(result * 100).toFixed(props.precision)} %`;
} else {
return `${result.toFixed(props.precision)} %`;
}
}
return `${result.toFixed(props.precision)} ${units[index]}`;
}
result /= sclaeNum;
}
if (unitType === 'percent') {
return `${result.toFixed(props.precision)} %`;
}
return `${result.toFixed(props.precision)} Yi`;
};
// 格式化持续时间单位的辅助函数
const beautifyDurationUnit = (num: string): string => {
let result = parseFloat(num);
const units = ['ns', 'us', 'ms', 's', 'm', 'h', 'd', 'w'];
let sclaeNum = 1000;
for (const index in units) {
if (parseInt(index) < 3) {
sclaeNum = 1000;
} else if (parseInt(index) < 5) {
sclaeNum = 60;
} else if (parseInt(index) < 6) {
sclaeNum = 24;
} else {
sclaeNum = 7;
}
if (Math.abs(result) <= sclaeNum || parseInt(index) === 7) {
return `${result.toFixed(props.precision)} ${units[index]}`;
}
result /= sclaeNum;
}
return `${result.toFixed(props.precision)} Yi`;
};
// 所有单位类型及其对应的单位数组
const allUnit = {
short: ['n', 'u', 'm', '', 'K', 'Mil', 'Bil', 'Tri'],
bytes: ['B', 'KB', 'MB', 'GB', 'TB', 'PB'],
'bytes/sec': ['B/s', 'KB/s', 'MB/s', 'GB/s', 'TB/s', 'PB/s'],
duration: ['ns', 'us', 'ms', 's', 'm', 'h', 'd', 'w'],
percent: ['0-100', '0.0-1.0'],
cpu: ['n', 'u', 'm', 'core', 'k'],
memory: ['B', 'Ki', 'Mi', 'Gi', 'Ti', 'Pi', 'Ei', 'Zi'],
storage: ['B', 'Ki', 'Mi', 'Gi', 'Ti', 'Pi', 'Ei', 'Zi'],
network: ['bps', 'Kbps', 'Mbps', 'Gbps'],
timecost: ['us', 'ms', 's'],
reqrate: ['req/s'],
count: ['', 'k', 'm'],
};
End
通过上面的代码,相信你就可以实现页面可视化,本文中所有代码均来自于开源项目,欢迎大家支持
https://github.com/kubegems/dashboard
